Next: 11. Exceptions Up: 1 The Pascal language Previous: 9. Operator overloading
The program header is provided for backwards compatibility, and is ignored by the compiler. The uses clause serves to identify all units that are needed by the program. The system unit doesn't have to be in this list, since it is always loaded by the compiler. The order in which the units appear is significant, it determines in which order they are initialized. Units are initialized in the same order as they appear in the uses clause. Identifiers are searched in the opposite order, i.e. when the compiler searches for an identifier, then it looks first in the last unit in the uses clause, then the last but one, and so on. This is important in case two units declare different types with the same identifier. When the compiler looks for unit files, it adds the extension .ppu (.ppw for Win32 platforms) to the name of the unit. On LINUX, unit names are converted to all lowercase when looking for a unit.
Programs

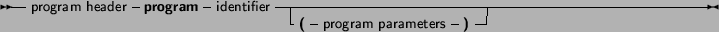

![\begin{syntdiag}\setlength{\sdmidskip}{.5em}\sffamily\sloppy \synt{uses\ clause}
\lit*{uses} \<[b] \synt{identifier} \\ \lit* , \> \lit* ;\end{syntdiag}](img133.png)
If a unit name is longer than 8 characters, the compiler will first look for a unit name with this length, and then it will truncate the name to 8 characters and look for it again. For compatibility reasons, this is also true on platforms that suport long file names.
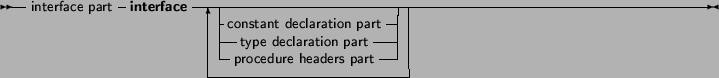
The interface part declares all identifiers that must be exported from the unit. This can be constant, type or variable identifiers, and also procedure or function identifier declarations. Declarations inside the implementation part are not accessible outside the unit. The implementation must contain a function declaration for each function or procedure that is declared in the interface part. If a function is declared in the interface part, but no declaration of that function is present in the implementation part, then the compiler will give an error.
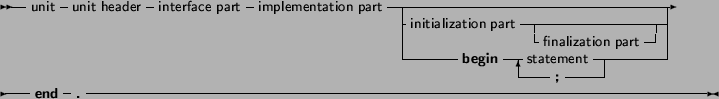
Units



![\begin{syntdiag}\setlength{\sdmidskip}{.5em}\sffamily\sloppy \synt{initializatio...
...art}
\lit*{initialization}
\<[b] \synt{statement} \\ \lit* ; \>\end{syntdiag}](img139.png)
![\begin{syntdiag}\setlength{\sdmidskip}{.5em}\sffamily\sloppy \synt{finalization\ part}
\lit*{finalization}
\<[b] \synt{statement} \\ \lit* ; \>\end{syntdiag}](img140.png)
When a program uses a unit (say unitA) and this units uses a second unit, say unitB, then the program depends indirectly also on unitB. This means that the compiler must have access to unitB when trying to compile the program. If the unit is not present at compile time, an error occurs.
Note that the identifiers from a unit on which a program depends indirectly, are not accessible to the program. To have access to the identifiers of a unit, you must put that unit in the uses clause of the program or unit where you want to yuse the identifier.
Units can be mutually dependent, that is, they can reference each other in their uses clauses. This is allowed, on the condition that at least one of the references is in the implementation section of the unit. This also holds for indirect mutually dependent units.
If it is possible to start from one interface uses clause of a unit, and to return there via uses clauses of interfaces only, then there is circular unit dependence, and the compiler will generate an error. As and example : the following is not allowed:
Unit UnitA; interface Uses UnitB; implementation end. Unit UnitB interface Uses UnitA; implementation end.But this is allowed :
Unit UnitA; interface Uses UnitB; implementation end. Unit UnitB implementation Uses UnitA; end.Because UnitB uses UnitA only in it's implentation section. In general, it is a bad idea to have circular unit dependencies, even if it is only in implementation sections.
Labels that can be used to identify statements in a block are declared in the label declaration part of that block. Each label can only identify one statement. Constants that are to be used only in one block should be declared in that block's constant declaration part. Variables that are to be used only in one block should be declared in that block's constant declaration part. Types that are to be used only in one block should be declared in that block's constant declaration part. Lastly, functions and procedures that will be used in that block can be declared in the procedure/function declaration part. After the different declaration parts comes the statement part. This contains any actions that the block should execute. All identifiers declared before the statement part can be used in that statement part.
Blocks


![\begin{syntdiag}\setlength{\sdmidskip}{.5em}\sffamily\sloppy \synt{label\ declaration\ part}
\lit*{label}
\<[b]
\synt{label}\\
\lit* ,
\>
\lit* ;\end{syntdiag}](img143.png)

![\begin{syntdiag}\setlength{\sdmidskip}{.5em}\sffamily\sloppy \synt{resourcestrin...
...{resourcestring}
\<[b]
\synt{string\ constant\ declaration}\\
\>\end{syntdiag}](img145.png)
![\begin{syntdiag}\setlength{\sdmidskip}{.5em}\sffamily\sloppy \synt{type\ declaration\ part}
\lit*{type}
\<[b]
\synt{type\ declaration}\\
\>\end{syntdiag}](img146.png)
![\begin{syntdiag}\setlength{\sdmidskip}{.5em}\sffamily\sloppy \synt{variable\ declaration\ part}
\lit*{var}
\<[b]
\synt{variable\ declaration}\\
\>\end{syntdiag}](img147.png)


Program Demo;
Var X : Real;
{ X is real variable }
Procedure NewDeclaration
Var X : Integer; { Redeclare X as integer}
begin
// X := 1.234; {would give an error when trying to compile}
X := 10; { Correct assigment}
end;
{ From here on, X is Real again}
begin
X := 2.468;
end.
In this example, inside the procedure, X denotes an integer variable.
It has it's own storage space, independent of the variable X outside
the procedure.
unit unitA;
interface
Type
MyType = Real;
implementation
end.
Program prog;
Uses UnitA;
{ Redeclaration of MyType}
Type MyType = Integer;
Var A : Mytype; { Will be Integer }
B : UnitA.MyType { Will be real }
begin
end.
This is especially useful if you redeclare the system unit's identifiers.
A Library is just like a unit or a program:
Libraries
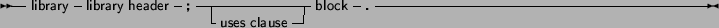

By default, functions and procedures that are declared and implemented in library are not available to a programmer that wishes to use your library.
In order to make functions or procedures available from the library, you must export them in an export clause:
Exports clause

![\begin{syntdiag}\setlength{\sdmidskip}{.5em}\sffamily\sloppy \synt{exports\ list}
\<[b] \synt{exports\ entry} \\ \lit* , \>\end{syntdiag}](img153.png)
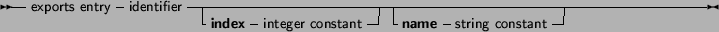
Under Win32, an index clause can be added to an exports entry. an index entry must be a positive number larger or equal than 1. It is best to use low index values, although nothing forces you to do this.
Optionally, an exports entry can have a name specifier. If present, the name specifier gives the exact name (case sensitive) of the function in the library.
If neither of these constructs is present, the functions or procedures are exported with the exact names as specified in the exports clause.